Data Science (or more specifically Data mining) has been
used for a long time for business oriented applications and solutions, namely
stock trading, credit scoring, and mail service optimization, among others. For
these activities, a lot of data has to be processed, in order to see patterns
and tendencies of individuals or singular entities (Read, 2010) .
With the rising of cheap computational power and fast
internet connections, Data science approaches for these activities are ideal,
because they provide an integrated framework to process large amount of data,
and learn from the data in a very optimized way, with a reduced interaction
from human beings; after setting the attributes for creating the model, they
let the machines learn, analyze, create the model, allowing analyst to evaluate
the model.
From Business to Scientific Research
But a very important characteristic of Data mining
approaches is the ability to extract human readable rules from the data,
significant from a statistical point of view, which an expert can evaluate and
use for practical purposes (Embcrechts, et al., 2005) .
In science, a great part researching is analyzing great
amount of data to support or refute hypothesis, and to find discernable
patterns. We can take the example of pattern recognition of brain scans or
electrocardiograms, to find problems or detect defect that might give us some
insight on early detection of abnormalities. (Vasileios, et al., 2000)
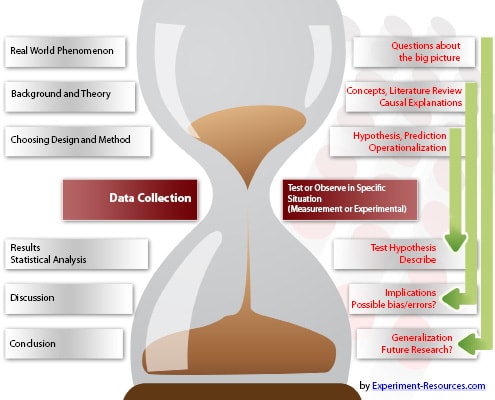
Figure 1
– Steps of the Scientific Process (Shuttleworth, 2013)
And that’s when Data Science comes into play, giving the
power and flexibility of deriving patterns from the enormous amount of data, in
a fraction of the time.
Bioinformatics: Data science to Save Lives
For a long time, scientist researching potential cures and
early detection technique for diseases have relied on visual identification of
patterns in acquired tissue samples, analyzed through microscopes and medical
devices in laboratories, which sometimes took a lot of time.
But now several enterprises and researchers are shifting
from that paradigm to the Data science approach. We can name the research of
the University of California, Santa Cruz (Schatz, 2015) . With traditional procedures, doctors
have conducted treatment of cancerous tumors depending on the part of the body
it presents itself. But UCSC is working on a Cancer Genome atlas to process and
cross reference tumors and is trying to find similarities among seemingly
different types of cancer, to improve detection and treatment.

Figure 2
– Bioinformatics Twitter Hashtags (Bioinformatics Jobs, 2016)
We can also mention the case of pharmaceutical conglomerate
Novartis, who made great advances in the field of detecting kidney disease. The
company claimed that a team, resulting from a coalition with Necker Children’s
Hospital-Imagine Foundation in Paris discovered a previously unnoticed gene
abnormality that caused focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in just six weeks,
using Big Data (Brien, 2013) .
Certainly, there’s no shortage of Big Data advancements in
the field of Bioinformatics, with numerous companies actively developing and
using Data Science Software for research (KDnuggets, 2000) .
Unveiling the Cosmos with Data Science
The vast immensity of the universe makes its study a prime
field for Big Data. The amount of data produced can reach 25 Zetta-bytes a year, doubling each year,
according to Moore’s law (Stephens, et al., 2015) . These levels of
information have been reached thanks to advances in telescope building and
detectors sensitivity.
Figure 3
– Four Domains of Big Data (Stephens, et al., 2015)
But the problem is not only in storage, but also in
processing. That is why projects such as GALEX and Kepler Space Telescope have
enormous data and image processing frameworks, and ALMA and Square Kilometer
Array projects have bigger data infrastructure planned (Andersen,
2012) .
Moving Physics to Hyper Drive
The CERN has been active in media outlets with its latest
discoveries, which incurs in the big problem of having extremely large sets of
data to go through. But thanks to its data processing frameworks and capabilities,
it has succeeded in numerous discoveries, including the Higgs boson discovery
with its Large Hadron Collider and Daya Bay Reactor Neutrino Experiment, which
looks to acquire better understanding neutrino, a subatomic produced by
decaying radioactive elements (Prabhat, 2015)
These endeavors have been so successful, CERN is planning on
expanding its Big Data analysis framework, by updating its detectors and
processing units in the hopes of improving its understanding of dark matter (University of
Bristol, 2016) .
Data Science in the Aid of All Sciences
These are only examples of scientific players that entered
the Data Science game, but any field that has large amounts of data can take
advantage of big data processing and prediction models
Data Science is even present in scientific researching as a
whole, with a company called Iris AI, which developed a machine learning
algorithm that allows researchers to find relevant publications by inputting a
text explaining the subject at hand (Frank, 2016) .
Figure 4
– Data Processing approach used at CERN (Jones, 2011)
So it is only a matter of time until other disciplines adopt
Data Science as an intrinsic part of the scientific process of research and
discovery.
Bibliography
Andersen, R., 2012. How Big Data Is Changing
Astronomy (Again). [Online]
Available at: http://www.theatlantic.com/technology/archive/2012/04/how-big-data-is-changing-astronomy-again/255917/
[Accessed May 2016].
Available at: http://www.theatlantic.com/technology/archive/2012/04/how-big-data-is-changing-astronomy-again/255917/
[Accessed May 2016].
Bioinformatics
Jobs, 2016. Twitter. [Online]
Available at: https://twitter.com/bioinformaticsj
[Accessed May 2016].
Available at: https://twitter.com/bioinformaticsj
[Accessed May 2016].
Brien, T.
O., 2013. Surfing the wave of big data analytics. [Online]
Available at: https://www.novartis.com/stories/discovery/surfing-wave-big-data-analytics
[Accessed May 2016].
Available at: https://www.novartis.com/stories/discovery/surfing-wave-big-data-analytics
[Accessed May 2016].
Embcrechts,
Szymanski & Sternickel, 2005. Chapter 10: Introduction to Scientific Data
Mining. In: Computationally Intelligent Hybrid Systems. New York:
s.n., pp. 317-365.
Frank, A.,
2016. Machine Learning’s Next Trick Will Transform How Research Is Done. [Online]
Available at: http://singularityhub.com/2016/05/26/machine-learnings-next-trick-will-transform-how-research-is-done/
[Accessed May 2016].
Available at: http://singularityhub.com/2016/05/26/machine-learnings-next-trick-will-transform-how-research-is-done/
[Accessed May 2016].
Jones, B.,
2011. Massive Computing at CERN and lessons learnt. [Online]
Available at: http://slideplayer.com/slide/6388912/
[Accessed May 2016].
Available at: http://slideplayer.com/slide/6388912/
[Accessed May 2016].
KDnuggets,
2000. Bioinformatics Companies. [Online]
Available at: http://www.kdnuggets.com/companies/bioinformatics.html
[Accessed February 2016].
Available at: http://www.kdnuggets.com/companies/bioinformatics.html
[Accessed February 2016].
Prabhat,
2015. Big science problems, big data solutions. [Online]
Available at: https://www.oreilly.com/ideas/big-science-problems-big-data-solutions
[Accessed May 2016].
Available at: https://www.oreilly.com/ideas/big-science-problems-big-data-solutions
[Accessed May 2016].
Read, B.,
2010. Data Mining and Science?. [Online]
Available at: http://www.ercim.eu/publication/ws-proceedings/12th-EDRG/EDRG12_Re.pdf
[Accessed May 2016].
Available at: http://www.ercim.eu/publication/ws-proceedings/12th-EDRG/EDRG12_Re.pdf
[Accessed May 2016].
Schatz, R.
D., 2015. Decoding and Defeating Cancer with Data Science. [Online]
Available at: http://www.slate.com/articles/health_and_science/ucsc2015/2015/04/decoding_and_defeating_cancer_with_data_science.html
[Accessed May 2016].
Available at: http://www.slate.com/articles/health_and_science/ucsc2015/2015/04/decoding_and_defeating_cancer_with_data_science.html
[Accessed May 2016].
Shuttleworth,
M., 2013. What is Research?. [Online]
Available at: https://explorable.com/what-is-research
[Accessed May 2016].
Available at: https://explorable.com/what-is-research
[Accessed May 2016].
Stephens, et
al., 2015. Big Data: Astronomical or Genomical?. [Online]
Available at: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.1002195
[Accessed May 2016].
Available at: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.1002195
[Accessed May 2016].
University
of Bristol, 2016. Dark Matter search enhanced by LHC’s new turbocharged
‘Brain’. [Online]
Available at: http://www.bristol.ac.uk/news/2016/may/dark-matter-search.html
[Accessed May 2016].
Available at: http://www.bristol.ac.uk/news/2016/may/dark-matter-search.html
[Accessed May 2016].
Vasileios,
et al., 2000. Data mining in brain imaging - Abstract. [Online]
Available at: http://smm.sagepub.com/content/9/4/359.abstract
[Accessed 2016 May].
Available at: http://smm.sagepub.com/content/9/4/359.abstract
[Accessed 2016 May].


